E-commerce SEO is the foundation for maximizing organic visibility and driving qualified traffic to online stores. Unlike general SEO, e-commerce SEO demands precise strategies tailored to product-heavy sites with extensive inventories and multiple categories. It’s about connecting with customers at every stage of their journey, from initial search to purchase, to drive measurable results that impact the bottom line.
This guide unpacks everything from keyword strategy to advanced technical SEO, delivering tactics that seasoned experts use to consistently outrank the competition.
Let’s dive right in!
Why E-commerce SEO Matters
E-commerce is hyper-competitive: more than 75% of searchers never go past the first page on Google, and 65% of all clicks go to the top five results.
SEO directly correlates with sales, well-optimized sites capture more organic traffic, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates.
Strategic Keyword Research for E-commerce
a. Comprehensive Keyword Mapping for the E-commerce Buyer’s Journey
Keyword research for e-commerce needs to move beyond generic volume-focused approaches. Instead, a mapped strategy should address awareness, consideration, and decision stages. By targeting keywords at each step of the buyer’s journey, e-commerce businesses can build relevance and trust, guiding users smoothly from research to purchase.
1. Awareness Stage: Target broader, informational keywords that address a potential customer’s needs or pain points.
For example, if you’re selling sustainable clothing, keywords like “benefits of eco-friendly clothing” or “how to choose sustainable fashion brands” are crucial.
2. Consideration Stage: Focus on more specific search intents such as “top sustainable clothing brands” or “best eco-friendly fabrics for summer,” which users commonly search during the evaluation phase.
3. Decision Stage: Target high-intent, transactional keywords such as “buy sustainable clothes online” or “organic cotton t-shirt shop.”
Using tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and AnswerThePublic, build keyword clusters that match searcher intent and include both short and long-tail keywords to maximize reach and relevance.
b. Competitive Gap Analysis & High-Intent Keyword Prioritization
To gain an edge over competitors, conduct a competitive gap analysis by identifying and targeting high-intent keywords they may be missing.
Tools like Ahrefs Content Gap and SEMrush’s Keyword Gap allow you to analyze top-performing pages of direct competitors, revealing keyword opportunities they haven’t optimized.
For example, if competitors are missing niche product-related terms like “affordable vegan leather bags,” capitalize on these by integrating them into product and category pages.
This kind of advanced keyword research enables you to craft a keyword strategy that captures both traffic and buyer intent. High-intent keywords generally show lower search volume but yield higher conversion rates, which is essential for e-commerce sites aiming to improve their ROI.
c. Product Fit and Relevance: Selecting Keywords that Drive Conversions
Choosing keywords relevant to both search intent and product fit can be a powerful way to optimize for conversions. This involves evaluating product pages and ensuring that they align with high-converting keywords.
For instance, targeting “ergonomic office chairs under $200” for a specific product ensures relevance and helps drive higher-intent traffic to that page. The idea here is to prioritize relevance over sheer volume, focusing on keywords that align closely with the product’s unique selling points.
Technical SEO for E-commerce Sites
a. Site Architecture & Crawlability
For e-commerce sites with extensive product catalogs, site architecture plays a crucial role in SEO. An ideal structure should allow both search engines and users to navigate easily through categories and products, enhancing crawlability and overall user experience.
A typical e-commerce site architecture might look like this:
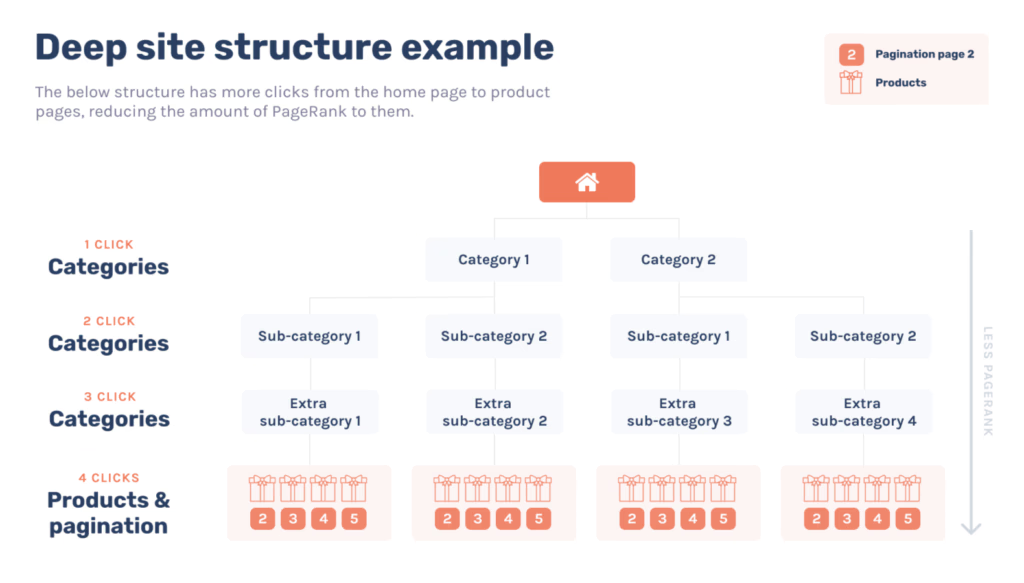
Source
Maintaining this hierarchy ensures that search engines can easily index all pages, avoiding orphaned pages and duplicate content issues.
Using breadcrumbs on every page also helps Google understand the site’s structure better, which can improve crawlability and site rankings.
b. Page Load Speed & Mobile Optimization
Page speed is essential for both user experience and SEO rankings. A one-second delay in page load time can lead to a 7% decrease in conversions, so optimizing page speed is non-negotiable. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix can provide insights on current page speed performance and suggest improvements.
For e-commerce sites, mobile optimization is equally critical. Statistics show that 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than three seconds to load.
Implement responsive design, compress images, and use accelerated mobile pages (AMP) to improve speed and functionality on mobile devices, ultimately enhancing rankings and engagement.
c. Schema Markup & Rich Snippets for E-commerce
Schema markup is one of the most overlooked but powerful tools for e-commerce SEO. By implementing Product Schema, Review Schema, and FAQ Schema on product and category pages, you can enhance search results with rich snippets, which increase CTRs significantly.

Source
For example, including reviews, star ratings, and pricing information can make your product pages more appealing directly within the SERPs, potentially increasing click-through rates by 10-30%.
Implementing Rich Snippets:
- Product Schema: Include product name, price, availability, and aggregate rating.
- Review Schema: Display star ratings and review counts, which are critical for competitive e-commerce markets.
- FAQ Schema: Answer common questions about the product or brand, making your pages more informative in search results.
On-page SEO for Product and Category Pages
a. Content Optimization Beyond Keywords
On-page SEO for product and category pages goes beyond keywords; it’s about creating an experience that resonates with customers’ needs and emotions.
To optimize these pages:
- Persuasive Product Descriptions: Craft descriptions that highlight benefits and emotional triggers rather than just product features. For example, rather than just describing a coffee maker as “stainless steel,” emphasize how it “delivers barista-quality coffee, every morning in the comfort of your home.” Using emotion and storytelling can make these pages more engaging and reduce bounce rates.
- Keyword Positioning for Conversions: Rather than stuffing keywords, prioritize a few high-converting keywords and include them naturally in titles, headers, and the first few sentences. Utilize modifiers like “best,” “top-rated,” or “affordable” to capture intent.
- Image Optimization and Alt Tags: High-quality images increase engagement. Include alt tags that describe the product using both keywords and unique descriptors, e.g., “eco-friendly organic cotton T-shirt in natural green.”
b. Product Schema & Reviews Integration
Integrating Product Schema and user-generated reviews can enhance visibility in search engines:
- Schema for Rich Snippets: Add structured data for Product Schema, such as availability, price, and ratings. This can make your listings more attractive in the SERP, increasing click-through rates.
- Leveraging Reviews with Schema: User-generated reviews are a goldmine for both engagement and SEO. Use Review Schema to show average ratings and review snippets in search results, which can increase clicks by up to 30%. Encourage customers to leave reviews, and feature them prominently on the product page, creating trust with future buyers.
c. Internal Linking Strategy
An optimized internal linking strategy connects users to related products, encourages upsells, and boosts SEO:
- Connect Related Products: Link to similar or complementary products to guide users through a natural buying journey, e.g., linking a camera product page to related accessories.
- Upsell Opportunities: Place links to higher-value items directly on product pages to encourage upsells. For instance, on a category page for backpacks, include a link to a premium backpack comparison guide.
- SEO Clusters: Structure links so that category pages, product pages, and blog content are interlinked. This enhances topic authority and makes pages easier for search engines to crawl.
Content Strategy for E-commerce SEO
a. SEO-Optimized Blog Content
An effective content strategy for e-commerce focuses on solving customer problems and building authority:
- How-to Guides and Industry Insights: Create educational blog posts tailored to each stage of the customer journey. For example, a retailer selling camping gear might post guides on “Beginner’s Guide to Camping,” “Best Lightweight Tents for Backpacking,” and “How to Pack a Sustainable Camping Kit.”
- Address Customer Pain Points: Content like “best practices,” “product comparisons,” and “beginner’s guides” directly addresses customer pain points and builds authority in your niche. Tools like AnswerThePublic can help identify common questions and keywords.
- Use Case Studies and Expert Reviews: These content types establish credibility, especially if you include real customer testimonials and reviews.
b. User-Generated Content (UGC)
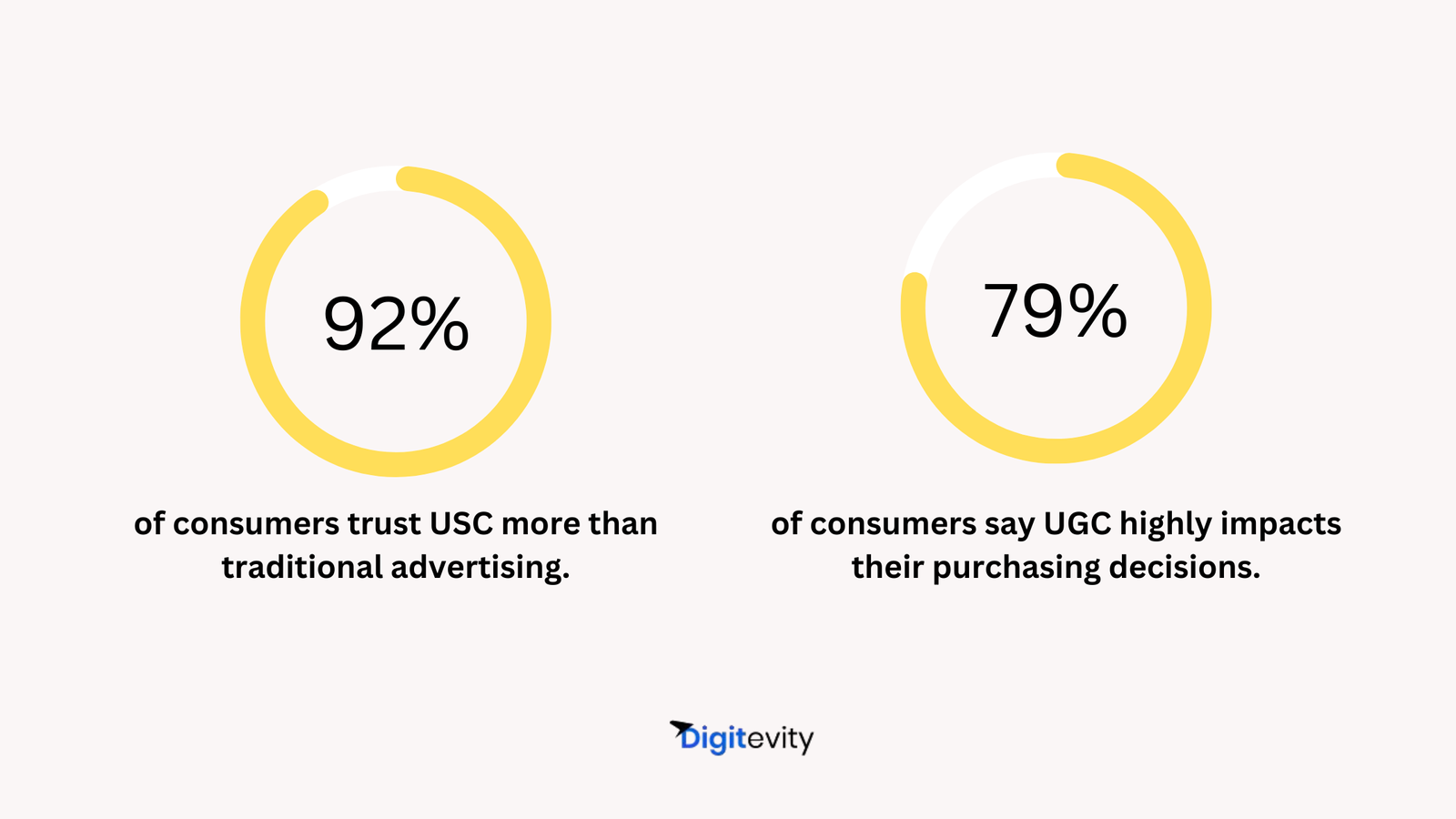
UGC is one of the most effective ways to bring fresh, authentic content to your site:
- Customer Testimonials and Photos: Encourage customers to share photos, reviews, and testimonials that can be featured on product pages and blog posts. Highlighting UGC not only increases engagement but also provides real-world validation.
- Social Media UGC: Curate customer content from platforms like Instagram and display it on your website to increase authenticity and trust.
- Incentivizing UGC: Offer incentives, like a discount or entry into a giveaway, to encourage customers to submit content. According to studies, 79% of people say UGC impacts their purchasing decisions.
c. Video SEO & Visual Content
Visual content, particularly video, enhances engagement and SEO performance:
- Product Demos and Tutorials: Product videos can improve conversions by up to 80% and reduce return rates by giving customers a realistic view of what they’re buying. Optimize videos by including keywords in video titles, descriptions, and tags.
- Optimize for Dwell Time: Videos keep users on the page longer, which is a positive ranking signal for search engines. Create how-to tutorials or brand story videos to increase engagement and conversions.
Advanced Link Building Strategies for E-commerce
a. Product Roundups & Influencer Collaborations
Collaborating with influencers and appearing in product roundups are powerful tactics to earn quality backlinks:
- Influencer Partnerships: Partner with industry influencers to reach a broader audience. Provide them with a free product sample or an affiliate commission for sharing content that links back to your site.
- Product Roundups on Authority Sites: Reach out to bloggers and media sites that publish “best of” product lists and ask to be included. These roundups not only provide a high-quality backlink but also target customers who are ready to buy.
- User Reviews on Social Channels: Ask influencers or loyal customers to review your products on their channels, linking back to the product page.
b. Digital PR & Content Syndication
Effective digital PR and content syndication can boost brand visibility and attract natural backlinks:
- Create Shareable Assets: Infographics, case studies, and unique data-driven research are highly shareable. For example, if you sell eco-friendly products, create an infographic on the environmental impact of conventional vs. sustainable materials.
- Content Syndication: Repurpose blog content on platforms like Medium and LinkedIn to extend reach and earn backlinks.
- Media Outreach: Contact relevant online publications with data-driven or newsworthy stories related to your products. For instance, if your product is trending or part of a new movement, media outlets are more likely to feature it.
c. Guest Blogging & Link Exchanges
Guest blogging and link exchanges with complementary brands can provide valuable backlinks:
- Target Complementary Brands for Link Exchanges: Reach out to non-competing brands with similar audiences, such as a hiking gear store linking to a camping cookware store, and establish a mutual linking strategy.
- Guest Posts on Industry Blogs: Offer to contribute expert content to industry-relevant blogs. Focus on writing valuable, niche-specific articles that link back to your category or product pages.
- Avoid Generic Link Exchanges: Quality matters over quantity. Stick to high-authority sites and partners that are relevant to your industry to ensure genuine value in your link-building strategy.
Leveraging Local SEO for E-commerce Growth (if applicable)
a. Google My Business & Local Listings
For e-commerce businesses with physical locations or regions they serve, Google My Business (GMB) can be a valuable asset:
- Setting Up GMB for Maximum Visibility: Optimize GMB profiles by using high-converting keywords in the business description, selecting accurate categories, and adding location-based images. Regular updates to posts and offers help maintain relevance.
- Local Listings: In addition to GMB, list your business on high-authority local directories, like Yelp, Bing Places, and Apple Maps. Each listing boosts visibility and enhances local ranking factors.
b. Location-Based Content
Tailored, location-specific content attracts local search traffic and builds brand relevance in specific areas:
- Geo-Targeted Landing Pages: Create landing pages specific to each city or region where your products or services are available. For instance, a furniture retailer might have separate pages for “Eco-Friendly Furniture in Austin, TX” and “Sustainable Home Decor in Boulder, CO.”
- Seasonal & Event-Based Content: Create blog posts or landing pages that address local seasonal trends, such as “Holiday Gift Ideas in Nashville” or “Best Winter Camping Gear for Denver.” This engages local customers while optimizing for region-specific search terms.
c. NAP Consistency & Local Citations
Maintaining consistent Name, Address, and Phone Number (NAP) information across listings is vital for local SEO:
- Check for Uniformity Across Listings: Use tools like Moz Local or Yext to audit NAP consistency. Uniform details across directories establish credibility and reduce the risk of ranking penalties.
- Building Local Citations: Prioritize high-quality citations from local directories, industry-specific listings, and chambers of commerce sites to improve your local SEO.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) Integrated with SEO
a. Optimized Checkout Processes
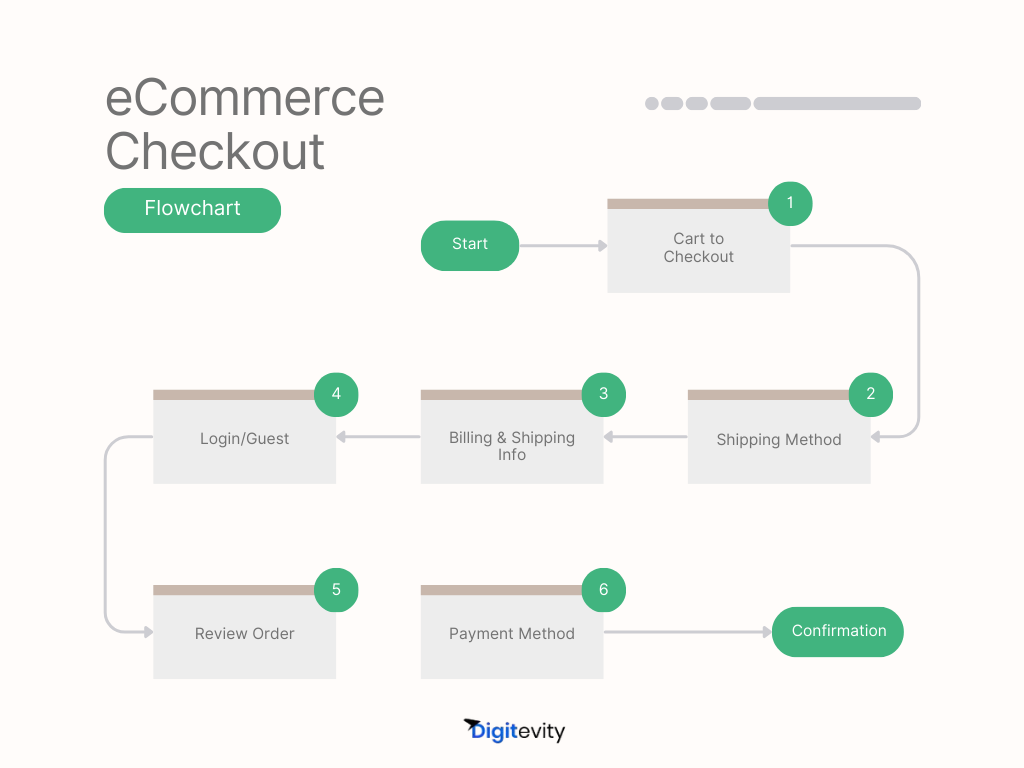
A smooth, optimized checkout process is essential to reduce cart abandonment:
- Streamline the Checkout Flow: Simplify the process by reducing the number of steps and offering a guest checkout option. Keeping secure, trusted payment methods and highlighting security cues (such as SSL badges) can increase buyer confidence.
- Site Speed Optimization: Slow pages often lead to high abandonment rates. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix to identify and fix performance issues.
b. A/B Testing for SEO and CRO
A/B testing allows you to refine pages to increase conversions while supporting SEO efforts:
- Testing Headlines, CTAs, and Page Layouts: Test variations of page headlines, product descriptions, and calls-to-action to discover which combinations drive the most engagement. Experiment with different layouts, such as sidebar vs. full-width designs, to see what improves conversion rates.
- Analyze the SEO Impact of Each Test: While testing, use analytics to track both conversion metrics and keyword rankings, ensuring that changes positively impact both SEO and user experience.
c. Customer Feedback Loops
Regular feedback from customers can help fine-tune product pages and improve the overall user experience:
- Survey Tools: Tools like Qualaroo and Hotjar can collect direct feedback from customers on the site. Use insights from customer responses to identify gaps in product information or areas for improvement.
- Add Feedback into Product Pages: For example, if customers frequently ask for more size details, update product pages to include a comprehensive sizing guide, enhancing usability and reducing returns.
Analytics & Performance Tracking for E-commerce SEO
a. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for E-commerce
Monitoring the right KPIs is crucial to assess the effectiveness of your SEO strategy:
- Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of visitors who complete a purchase. A low conversion rate often indicates issues with site usability or checkout flow.
- Average Order Value (AOV): Understanding AOV helps in determining the effectiveness of upselling and cross-selling tactics.
- Organic Traffic Growth: Track the increase in organic traffic over time, using filters to analyze by product pages, blog content, or location-based traffic sources.
b. SEO Tool Stack Optimization
Using the right tools helps refine strategy and monitor performance:
- Google Analytics & Google Search Console: Analyze user behavior, track conversion paths, and monitor keyword rankings. These tools provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of on-page optimizations.
- Heatmaps & User Behavior Tools: Hotjar or Crazy Egg can visualize user interactions, showing where visitors click, scroll, or drop off, which informs layout adjustments to improve engagement and reduce bounce rates.
b. Periodic SEO Audits and Adjustments
Conducting regular SEO audits ensures your site maintains top performance:
- Quarterly Audits for Performance Checks: Use tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush for in-depth audits every quarter. Check for issues like broken links, duplicate content, and page load times, addressing them to maintain a high SEO score.
- Identify and Improve Weak Pages: Analyze low-performing pages and make improvements to increase ranking and user engagement, such as by adding more detailed descriptions or high-quality images.
E-commerce SEO Pitfalls to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes can save e-commerce businesses from drops in rankings or user dissatisfaction:
- Duplicate Content: Duplicate content across product pages or categories can lead to ranking penalties. Address this by using canonical tags and creating unique descriptions for each product.
- Slow Page Speed: A slow site affects rankings and conversions. Compress images, leverage browser caching, and consider a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to speed up load times.
- Poor Mobile Experience: Over 50% of e-commerce traffic comes from mobile devices. Ensure your site is mobile-responsive with an optimized design that prioritizes ease of use, fast loading, and intuitive navigation.
Conclusion and Next Steps
SEO should be approached holistically. It’s more than just keywords; it’s about creating an experience that aligns with the needs of both search engines and customers.
Encourage businesses to view SEO as an evolving process. As algorithms change, so should your strategies, adapting to new search trends and customer behaviors to stay ahead in an ever-evolving marketplace.




